
The balance sheet is the “heart” of the system of financial reporting – where reflects the overall situation, assets, liabilities, equity of the business at a certain time. Particularly in the context of conversion of standardized accounting system, internal understanding how to set up the balance sheet not only is the responsibility of the accountants, but also the necessities of the management board, the business owner.
Many enterprises when deploying solutions accounting assets often have difficulty in the synthesis of data, classification of assets, or disposal of materials depreciation to put on the balance sheet standard. Therefore, this article will help you understand from theory to practices on how to set up the balance sheet, including the structure, principle, process, step by step, the important note – ensure correct standard circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC.
1. Why business need to understand how to create balance sheet?
Balance sheet (Balance Sheet) is not only a form required in the financial statements, but also are important tools to:
- Reviews financial capacity fact: Total assets, debt ratio, equity,... is the important indicator to help administrators, investors, bank decisions.
- Orientation internal management: resource allocation, capital control, fixed assets, optimize cash flow.
- Compliance with legal regulation: Is one of the four mandatory reporting must be submitted annually under circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC.
Especially with the ongoing business accounting software assets, the balance sheet is the convergence property data recorded increased, reduced, depreciation, collated with the capital, liabilities – to form a circle accounting closed, transparent.
Read more:
2. Balance sheet what is it? Structure and principle establishment
The concept of the balance sheet according to standard accounting Vietnam (VAS)
Under circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC, the balance sheet is a financial report aggregate, reflect the assets, capital of the business at a certain time (usually the end of the accounting period). Consists of 2 main parts:
- Property: reflecting the full value that the business owns or control.
- Sources of funds (Liabilities + Equity): reflects the source form of that property.
The relationship between the two parts is expressed by formula accounting classics: Total assets = Total liabilities + Equity
This is the basis to ensure the “balance” of the table – means there's always a correspondence between resources, formation resources that.
Accounting principles - the formula weight for basic
When drawing up the balance sheet, accounting students need to adhere to the principles of basic accounting as:
- Principle cost: Assets are recorded at cost initially, not according to the market price.
- Principle of consistency: the Method of classification, recognition must maintain stable over the accounting period.
- Principle of materiality: Priority presenting the items important influence the economic decisions of users report.
- Guidelines for the dual: All accounting profession must affect at least two accounts with ties for applications.
Compliance with these principles not only help ensure the accuracy and transparency of reporting, but also help data have the ability to collate, audit, integration with system accounting software modern.
Structure of the balance sheet according to circular 200
Balance sheet form B01-DN includes 2 large portions:
I. Assets- Short-term assets (Code 100): Cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, inventory, accounts receivable,...
- Long-term assets (Code 200): fixed Assets tangible, intangible, real estate investments, prepaid expenses, long-term...
- Liabilities (Code 300): include short-term debt (payables, short term loans, tax payable), long-term debt.
- Equity (Code 400): contributed Capital, retained earnings, investment funds, development,...
Each of the indicators in the table are attached code, interpret the columns show data for current year, previous year – to help compare, evaluate financial trends.

3. The detailed steps to perform the way the balance sheet for business accounting
To be a balance sheet accounting standards, the accountant should comply with a process that consists of 4 basic steps in which the first step is the foundation important to ensure data accuracy and transparency.
DOWNLOAD SAMPLE BALANCE SHEET EXCEL STANDARD CIRCULAR 200 FREE
Step 1: collect accounting data from books, the system property
This is the first step, but is also the most important factor in setting up the balance sheet. Business need:
- Reviewing the entire financial data end of the period: the balance of the account from 111 to 338, pay special attention to the asset account as 211 (fixed assets tangible), 213 (fixed assets intangible), 131 (receivable), 331 (pay), 333 (tax).
- Extract data from accounting software property: for business has implemented accounting system property (as AccNet Asset), the business recorded an increase in recording, reduce, adjust the property values will be synchronized to accurately recorded on the balance sheet.
- Ensures data transfer: the entry end of the period, such as allocation of prepaid expenses, depreciation of fixed assets, the transfer pnl... must be made in full to data valid.
Note: For businesses that have large scale, need to prepare the table aggregate assets by category, making it easy to group on each item of the balance sheet.
Step 2: Classification of assets - capital standards circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC
The correct classification helps balance sheet, obviously, avoid errors frequently encountered when the confusion between short-term and long-term. Specific:
Property:
- Short term: includes cash, bank deposits, short-term investments, accounts receivable, customer, inventory, prepaid expenses short-term.
- Long-term: includes fixed assets (fixed assets), real estate investments, prepaid expenses, long-term investment capital contributions long-term assets in progress long-term.
Capital:
Liabilities:
- Short term: Payables, short-term loans, buyers pay in advance, the tax payable.
- Long term: Long-term loans, issuing bonds, fund development,...
Equity: includes capital contributed by owners, capital surplus, retained earnings, the fund's internal business. Note: Items as “cost of uncompleted construction”, “investment long term financial” or “the science development foundation” is often incorrectly classified if accountants do not understand the nature.
Step 3: Write final balance, check balance
After sorting is done, the accounting will be conducted:
- Take the final balance of each account from balance Sheet account accounting.
- Fill in each corresponding norm on the sample B01-DN – balance sheet accounting circular 200.
- Synthetic, check balance: Ensure that: Total assets = Total capital
If there are deviations, need to check account balances, journal entries the transfer end or misidentification of the account short-term/long-term.
Tips: Use of accounting software has the function of automatic checking balance will help shorten the duration collation, reduce risk tolerances.
Step 4: Set up the balance sheet according to the sample format standard
Enterprises need to use sample B01-DN issued together with circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC, with the columns:
- Norm (item name)
- Code
- Overs (if available)
- The last number states
- Beginning balance
After filling all the data, the accountant should:
- Format clear presentation logic.
- Endorsed by the establishment – chief accountant – legal representative.
- Stored according to the correct specified time (minimum 10 years with financial statements).

4. Some note and errors frequently encountered when the balance sheet accounting
How to set up the balance sheet seemingly simple but often make the common mistake, seriously affect the quality of financial reporting.
Not correct classification term assets – capital
- Confusion between short-term and long-term, especially in the accounts receivable long-term loans long-term.
- Fixed assets are liquidated, waiting for the transfer back recorded in the property are used.
- Write the wrong account 128 (short term investment) of 228 (long-term), causing deviations of total assets.
Not update the data depreciation, revaluation of assets
- Fixed assets have not been depreciated in full → increase the value of virtual assets.
- Do not re-adjust the residual value of the asset after revaluation or liquidation → affect the balance sheet, the statement of the business.
- Teen recorded wear with assets finance lease or record the wrong property owned outside.
Skewed data due to accounting wrong or not adjust the shipping
- Not yet turning a profit last period on account 421 → false equity.
- False the account with account public debt (131, 331) → leads to data does not match the detail window.
- Forgot recorded INCOME tax payable, bonus – benefits,... affect the total equity.

5. Sample balance sheet accounting and illustrative examples practical
To easily visualize, apply, below is a sample balance sheet accounting standard under circular no. 200/2014/TT-BTC, for example simulation data for business, medium scale production.
Sample balance sheet accounting circular 200 (form B01-DN)
| INDICATORS | CODE | NOTES | THE LAST NUMBER STATES | BEGINNING BALANCE |
| A. ASSETS | ||||
| I. short-term Assets | 100 | |||
| 1. Cash and cash equivalents | 110 | -1 | 550.000.000 | 450.000.000 |
| 2. Accounts receivable, short-term | 130 | -2 | 1.200.000.000 | 1.000.000.000 |
| 3. Inventory | 140 | -3 | 2.300.000.000 | 2.000.000.000 |
| II. Long-term assets | 200 | |||
| 1. Fixed assets | 210 | -4 | 3.000.000.000 | 3.200.000.000 |
| 2. Investment long term financial | 250 | -5 | 500.000.000 | 500.000.000 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 270 | 7.550.000.000 | 7.150.000.000 | |
| B. CAPITAL | ||||
| I. Liabilities | 300 | |||
| 1. Pay the seller the short term | 310 | -6 | 1.500.000.000 | 1.200.000.000 |
| 2. Taxes and other payables to The state budget | 315 | -7 | 300.000.000 | 250.000.000 |
| 3. Long-term loans | 330 | -8 | 1.000.000.000 | 1.500.000.000 |
| II. Equity | 400 | |||
| 1. Capital contributed by the owner | 410 | 3.000.000.000 | 3.000.000.000 | |
| 2. Profit after tax has not distributed | 420 | 1.750.000.000 | 1.200.000.000 | |
| TOTAL CAPITAL RESOURCES | 440 | 7.550.000.000 | 7.150.000.000 |
Note: The column “notes” refers to the notes to financial statements – where explained in detail each item if there are large fluctuations.
Read more: Mẫu bảng thống kê biến động tài khoản trong kỳ kế toán
Practical examples for how to create a balance sheet for accounting: Business, medium scale production
A business specialized in manufacturing electrical equipment have data as follows:
- Fixed assets machinery: 5 billion, depreciation remaining 3 billion.
- Inventory raw material: 1.2 billion.
- Bank deposits: 0.5 billion.
- Current liabilities: 1.8 billion.
- Capital owners: 3 billion.
- Retained earnings: 2.5 billion.
→ The balance sheet will be recorded:
- Total assets = 0,5 + 1,2 + 3 (fixed assets) + other receivables
- Total capital = short-term debt + equity
When accounting software assets (for example AccNet Asset) was integrated, the entire data of fixed assets, depreciation, decrease in value, the shipping should automatically update – help set the table exactly, quickly, avoid errors crafts.
6. The optimal solution to help the balance sheet accounting accuracy and efficiency
Many businesses today still the balance sheet in Excel easy wrong number, loss of time, lack of data connection. The solution is use accounting software specializedspecial management module fixed assets, integrated report automatically. A number of benefits when applied software:
- Automatically record increase, reduced assets by invoice input, written test.
- Depreciation accurate monthly by different methods (straight line, declining balance,...).
- Sync data assets on the balance sheet, no need to enter manually.
- Establishment report form B01-DN, there are warning imbalance.
Typical example: Software AccNet ERP integrated accounting assets – general – finance, allowing the balance sheet in real time, assist in submission of reports through the network.
PHẦN MỀM KẾ TOÁN ACCNET ERP TÍCH HỢP “TRỢ LÝ TÀI CHÍNH AI”
With 7 phân hệ lõi tích hợp từ kế toán, bán hàng, mua hàng, sản xuất, kho vận, nhân sự đến phân phối, phần mềm quản lý doanh nghiệp AccNet ERP tạo nên một hệ sinh thái quản trị tài chính – điều hành khép kín, đồng bộ thông tin xuyên suốt:
- Tài chính – Kế toán: Quản lý quỹ, ngân hàng, tài sản, giá thành, công nợ, sổ sách tổng hợp. Hơn 100 mẫu báo cáo quản trị tài chính được cập nhật tự động, đúng chuẩn kế toán Việt Nam.
- Sales: Theo dõi chu trình bán hàng, từ báo giá, hợp đồng đến hóa đơn, cảnh báo công nợ, hợp đồng đến hạn.
- Mua hàng – Nhà cung cấp: Phê duyệt đa cấp, tự động tạo phiếu nhập kho từ email, kiểm tra chất lượng đầu vào.
- Kho vận – Tồn kho: Đối chiếu kho thực tế và sổ sách kế toán, kiểm soát bằng QRCode, RFIF, kiểm soát cận date, tồn kho chậm luân chuyển, phân tích hiệu quả sử dụng vốn.
- Sản xuất: Giám sát nguyên vật liệu, tiến độ sản xuất theo ca/kế hoạch, phân tích năng suất từng công đoạn.
- Phân phối – Bán lẻ: Kết nối máy quét mã vạch, máy in hóa đơn, đồng bộ tồn kho tại từng điểm bán theo thời gian thực.
- Nhân sự – Tiền lương: Theo dõi hồ sơ, tính lương thưởng, đánh giá hiệu suất, lập kế hoạch ngân sách nhân sự.
TÍCH HỢP TRỢ LÝ TÀI CHÍNH KẾ TOÁN AI - RA MẮT 2025
AccNet ERP là một nền tảng công nghệ mở, tích hợp các giải pháp tiên tiến như:
- Phân tích tài chính 24/7 trên cả desktop & mobile: Tư vấn tài chính dựa trên BI Financial Dashboard chứa số liệu thực tế chỉ trong vài phút.
- Dự báo xu hướng và rủi ro tài chính: Dự báo rủi ro, xu hướng về mọi chỉ số tài chính từ lịch sử dữ liệu. Đưa ra gợi ý, hỗ trợ ra quyết định.
- Tra cứu thông tin chỉ trong vài giây: Tìm nhanh tồn kho, công nợ, doanh thu, giá vốn, dòng tiền,… thông qua các cuộc trò chuyện
- Tự động nghiệp vụ hóa đơn/chứng từ: Nhập liệu hóa đơn, kiểm tra lỗi, thiết lập lịch hạch toán chứng từ, kết xuất file, gửi mail,...
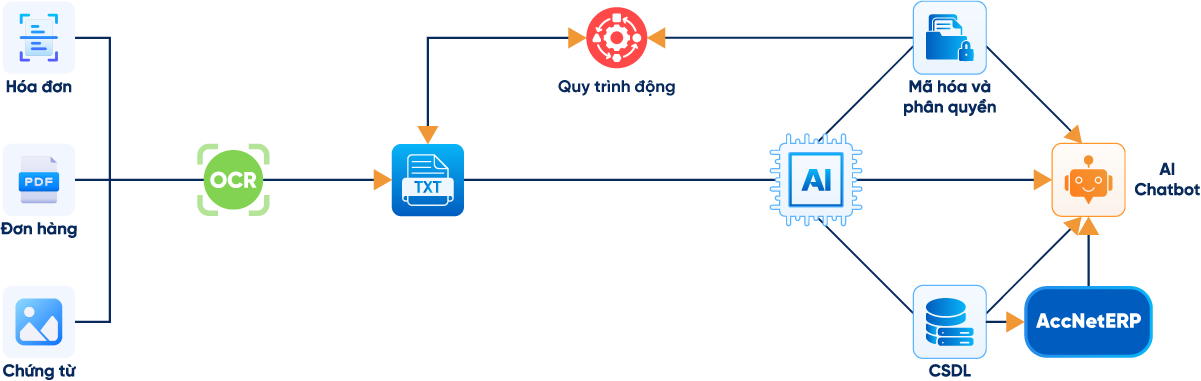
DOANH NGHIỆP ĐƯỢC GÌ KHI TRIỂN KHAI ACCNET ERP?
✅ Quản lý tài chính chủ động – Không còn “bơi trong số liệu rời rạc”
- Automate 80% of the accounting profession standards, the Ministry of Finance
- AI support phân tích báo cáo tài chính - Financial Dashboard real-time
- Đồng bộ dữ liệu real-time, mở rộng phân hệ linh hoạt & vận hành đa nền tảng
- Tích hợp ngân hàng điện tử, hóa đơn điện tử, phần mềm khác…, kết nối với hệ thống kê khai thuế HTKK
✅ Hiệu quả rõ rệt khi ứng dụng trợ lý tài chính AI
- Giảm 20–30% chi phí vận hành nhờ kiểm soát ngân sách theo từng phòng ban
- Tăng 40% hiệu quả sử dụng dòng tiền, dòng tiền ra/vào được cập nhật theo thời gian thực
- Thu hồi công nợ đúng hạn >95%reduce losses and bad debts
- Cut 50% aggregate time & financial analysis
- Business tiết kiệm từ 500 triệu đến 1 tỷ đồng/nămincrease the efficient use of capital when deploying AccNet ERP
ĐĂNG KÝ NHẬN DEMO NGAY
Vui lòng điền các thông tin vào form chúng tôi sẽ liên hệ lại với bạn trong 24h làm việc.
KHÁCH HÀNG TIÊU BIỂU ĐÃ VÀ ĐANG TRIỂN KHAI ACCNET ERP




















✅ Demo miễn phí full tính năng
✅ Báo giá cá nhân hóa theo quy mô doanh nghiệp
✅ Tư vấn 1:1 cùng chuyên gia có nhiều kinh nghiệm
How to set up the balance sheet not only is obliged to report, which is a tool to help businesses clearly see the “financial picture” at one time – from then on governance decisions, investment more effective. In particular, with the ongoing business accounting solution properties, the setup of the balance sheet as need to be precise, in sync.
To make the way of balance sheet efficiency, enterprises should:
- Build system clear account, updated periodically
- Classification of assets – capital in the correct circular
- Use accounting software integration property – synthesis – finance
- Automation, reports, control data frequently
You are in need of the balance sheet accounting express – standard – right model? Trải nghiệm ngay AccNet ERP – Phần mềm kế toán toàn diệnto help you plan your report B01-DN in just a few clicks!
CONTACT INFORMATION:
- ACCOUNTING SOLUTIONS COMPREHENSIVE ACCNET
Headquarters: 23 Nguyen Thi huynh, Ward 8, Phu Nhuan District, ho chi minh CITY.CITY
Hotline: 0901 555 063
Email: accnet@lacviet.com.vn
Website: https://accnet.vn/


Theme: